Go Data Structures: Binary Search Tree
Analysis and implementation of the Binary Search Tree data structure in Go
AI workshop
join cohort #1
A tree is a representation of a hierarchical structure. It’s easy to imagine a tree by thinking about a family genealogy tree.
Like a hash table or a graph, is a non-sequential data structure.
A binary tree is a tree where every node has max 2 children.
A binary search tree has the property of the left node having a value less than the value on the right node.
This is what we’ll build in this article. It’s a very useful data structure for efficient storing and indexing of data, and data retrieval.
Terminology
Root: the level 0 of the tree
Child: each node of the tree that’s not the root
Internal node: each node with at least a child
Leaf: each node that has no children
Subtree: the set of node with a certain node as root
Preliminary info
A binary search tree data structure will expose those methods:
Insert(t)inserts the Item t in the treeSearch(t)returns true if the Item t exists in the treeInOrderTraverse()visits all nodes with in-order traversingPreOrderTraverse()visits all nodes with pre-order traversingPostOrderTraverse()visits all nodes with post-order traversingMin()returns the Item with min value stored in the treeMax()returns the Item with max value stored in the treeRemove(t)removes the Item t from the treeString()prints a CLI readable rendering of the tree
I’ll create an ItemBinarySearchTree generic type, concurrency safe, that can generate trees containing any type by using genny, to create a type-specific tree implementation, encapsulating the actual value-specific data structure containing the data.
I define each note as
// Node a single node that composes the tree
type Node struct {
key int
value Item
left *Node //left
right *Node //right
}The key value allows to use any kind of Item type, and use a separate value for calculating the correct place. I implemented it as an integer, but it could take any type that can be compared.
Inserting an item into a tree requires the use of recursion, since we need to find the correct place for it. The rule is, if the key of the node is < than the current node tree, we put it as the left child, if there is no left child. Otherwise, we recalculate the position by using the left child as the base node. Same goes for the right child.
Traversing is the process of navigating the tree, and we implement 3 ways to do it, since there are 3 different approaches. Taken this binary search tree:
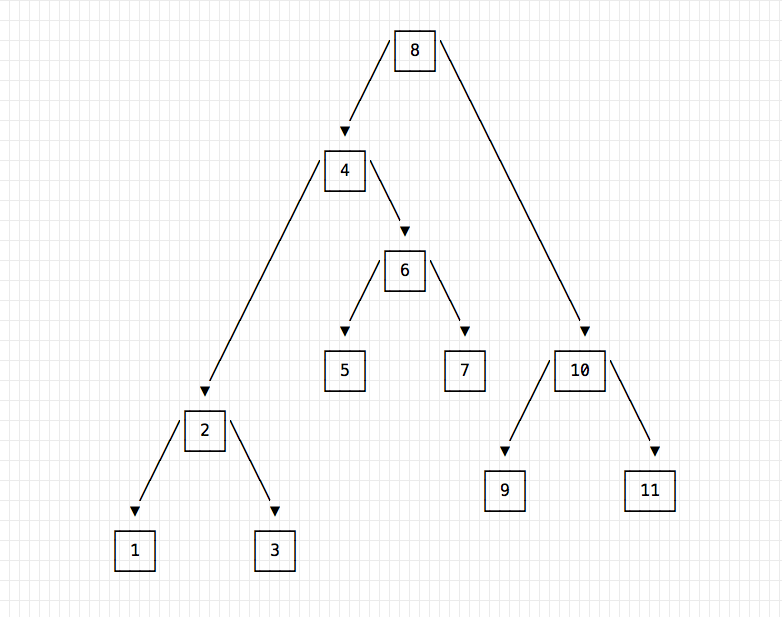
this is how we could traverse it:
- in-order: we visit all nodes by following the smallest link until we find the left-most leaf, then processes the leaf and moves to other nodes by going into the next smallest key value linked to the current one. In the above picture:
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> 9 -> 10 -> 11 - pre-order: before visiting the children, this approach visits the node first. In the above picture:
8 -> 4 -> 2 -> 1 -> 3 -> 6 -> 5 -> 7 -> 10 -> 9 -> 11 - post-order: we find the smallest leaf (the left-most one), then processes the sibling and then the parent node, then goes to the next subtree, and navigates up the parent. In the above picture:
1 -> 3 -> 2 -> 5 -> 7 -> 6 -> 4 -> 9 -> 11 -> 10 -> 8
The String method, used in the tests to have a visual feedback on the methods, will print the above tree as
------------------------------------------------
---[ 1
---[ 2
---[ 3
---[ 4
---[ 5
---[ 6
---[ 7
---[ 8
---[ 9
---[ 10
---[ 11
------------------------------------------------Implementation
// Package binarysearchtree creates a ItemBinarySearchTree data structure for the Item type
package binarysearchtree
import (
"fmt"
"sync"
"github.com/cheekybits/genny/generic"
)
// Item the type of the binary search tree
type Item generic.Type
// Node a single node that composes the tree
type Node struct {
key int
value Item
left *Node //left
right *Node //right
}
// ItemBinarySearchTree the binary search tree of Items
type ItemBinarySearchTree struct {
root *Node
lock sync.RWMutex
}
// Insert inserts the Item t in the tree
func (bst *ItemBinarySearchTree) Insert(key int, value Item) {
bst.lock.Lock()
defer bst.lock.Unlock()
n := &Node{key, value, nil, nil}
if bst.root == nil {
bst.root = n
} else {
insertNode(bst.root, n)
}
}
// internal function to find the correct place for a node in a tree
func insertNode(node, newNode *Node) {
if newNode.key < node.key {
if node.left == nil {
node.left = newNode
} else {
insertNode(node.left, newNode)
}
} else {
if node.right == nil {
node.right = newNode
} else {
insertNode(node.right, newNode)
}
}
}
// InOrderTraverse visits all nodes with in-order traversing
func (bst *ItemBinarySearchTree) InOrderTraverse(f func(Item)) {
bst.lock.RLock()
defer bst.lock.RUnlock()
inOrderTraverse(bst.root, f)
}
// internal recursive function to traverse in order
func inOrderTraverse(n *Node, f func(Item)) {
if n != nil {
inOrderTraverse(n.left, f)
f(n.value)
inOrderTraverse(n.right, f)
}
}
// PreOrderTraverse visits all nodes with pre-order traversing
func (bst *ItemBinarySearchTree) PreOrderTraverse(f func(Item)) {
bst.lock.Lock()
defer bst.lock.Unlock()
preOrderTraverse(bst.root, f)
}
// internal recursive function to traverse pre order
func preOrderTraverse(n *Node, f func(Item)) {
if n != nil {
f(n.value)
preOrderTraverse(n.left, f)
preOrderTraverse(n.right, f)
}
}
// PostOrderTraverse visits all nodes with post-order traversing
func (bst *ItemBinarySearchTree) PostOrderTraverse(f func(Item)) {
bst.lock.Lock()
defer bst.lock.Unlock()
postOrderTraverse(bst.root, f)
}
// internal recursive function to traverse post order
func postOrderTraverse(n *Node, f func(Item)) {
if n != nil {
postOrderTraverse(n.left, f)
postOrderTraverse(n.right, f)
f(n.value)
}
}
// Min returns the Item with min value stored in the tree
func (bst *ItemBinarySearchTree) Min() *Item {
bst.lock.RLock()
defer bst.lock.RUnlock()
n := bst.root
if n == nil {
return nil
}
for {
if n.left == nil {
return &n.value
}
n = n.left
}
}
// Max returns the Item with max value stored in the tree
func (bst *ItemBinarySearchTree) Max() *Item {
bst.lock.RLock()
defer bst.lock.RUnlock()
n := bst.root
if n == nil {
return nil
}
for {
if n.right == nil {
return &n.value
}
n = n.right
}
}
// Search returns true if the Item t exists in the tree
func (bst *ItemBinarySearchTree) Search(key int) bool {
bst.lock.RLock()
defer bst.lock.RUnlock()
return search(bst.root, key)
}
// internal recursive function to search an item in the tree
func search(n *Node, key int) bool {
if n == nil {
return false
}
if key < n.key {
return search(n.left, key)
}
if key > n.key {
return search(n.right, key)
}
return true
}
// Remove removes the Item with key `key` from the tree
func (bst *ItemBinarySearchTree) Remove(key int) {
bst.lock.Lock()
defer bst.lock.Unlock()
remove(bst.root, key)
}
// internal recursive function to remove an item
func remove(node *Node, key int) *Node {
if node == nil {
return nil
}
if key < node.key {
node.left = remove(node.left, key)
return node
}
if key > node.key {
node.right = remove(node.right, key)
return node
}
// key == node.key
if node.left == nil && node.right == nil {
node = nil
return nil
}
if node.left == nil {
node = node.right
return node
}
if node.right == nil {
node = node.left
return node
}
leftmostrightside := node.right
for {
//find smallest value on the right side
if leftmostrightside != nil && leftmostrightside.left != nil {
leftmostrightside = leftmostrightside.left
} else {
break
}
}
node.key, node.value = leftmostrightside.key, leftmostrightside.value
node.right = remove(node.right, node.key)
return node
}
// String prints a visual representation of the tree
func (bst *ItemBinarySearchTree) String() {
bst.lock.Lock()
defer bst.lock.Unlock()
fmt.Println("------------------------------------------------")
stringify(bst.root, 0)
fmt.Println("------------------------------------------------")
}
// internal recursive function to print a tree
func stringify(n *Node, level int) {
if n != nil {
format := ""
for i := 0; i < level; i++ {
format += " "
}
format += "---[ "
level++
stringify(n.left, level)
fmt.Printf(format+"%d\n", n.key)
stringify(n.right, level)
}
}Tests
The tests describe the usage of the above implementation.
package binarysearchtree
import (
"fmt"
"testing"
)
var bst ItemBinarySearchTree
func fillTree(bst *ItemBinarySearchTree) {
bst.Insert(8, "8")
bst.Insert(4, "4")
bst.Insert(10, "10")
bst.Insert(2, "2")
bst.Insert(6, "6")
bst.Insert(1, "1")
bst.Insert(3, "3")
bst.Insert(5, "5")
bst.Insert(7, "7")
bst.Insert(9, "9")
}
func TestInsert(t *testing.T) {
fillTree(&bst)
bst.String()
bst.Insert(11, "11")
bst.String()
}
// isSameSlice returns true if the 2 slices are identical
func isSameSlice(a, b []string) bool {
if a == nil && b == nil {
return true
}
if a == nil || b == nil {
return false
}
if len(a) != len(b) {
return false
}
for i := range a {
if a[i] != b[i] {
return false
}
}
return true
}
func TestInOrderTraverse(t *testing.T) {
var result []string
bst.InOrderTraverse(func(i Item) {
result = append(result, fmt.Sprintf("%s", i))
})
if !isSameSlice(result, []string{"1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "10", "11"}) {
t.Errorf("Traversal order incorrect, got %v", result)
}
}
func TestPreOrderTraverse(t *testing.T) {
var result []string
bst.PreOrderTraverse(func(i Item) {
result = append(result, fmt.Sprintf("%s", i))
})
if !isSameSlice(result, []string{"8", "4", "2", "1", "3", "6", "5", "7", "10", "9", "11"}) {
t.Errorf("Traversal order incorrect, got %v instead of %v", result, []string{"8", "4", "2", "1", "3", "6", "5", "7", "10", "9", "11"})
}
}
func TestPostOrderTraverse(t *testing.T) {
var result []string
bst.PostOrderTraverse(func(i Item) {
result = append(result, fmt.Sprintf("%s", i))
})
if !isSameSlice(result, []string{"1", "3", "2", "5", "7", "6", "4", "9", "11", "10", "8"}) {
t.Errorf("Traversal order incorrect, got %v instead of %v", result, []string{"1", "3", "2", "5", "7", "6", "4", "9", "11", "10", "8"})
}
}
func TestMin(t *testing.T) {
if fmt.Sprintf("%s", *bst.Min()) != "1" {
t.Errorf("min should be 1")
}
}
func TestMax(t *testing.T) {
if fmt.Sprintf("%s", *bst.Max()) != "11" {
t.Errorf("max should be 11")
}
}
func TestSearch(t *testing.T) {
if !bst.Search(1) || !bst.Search(8) || !bst.Search(11) {
t.Errorf("search not working")
}
}
func TestRemove(t *testing.T) {
bst.Remove(1)
if fmt.Sprintf("%s", *bst.Min()) != "2" {
t.Errorf("min should be 2")
}
}Creating a concrete tree data structure
You can use this generic implemenation to generate type-specific trees, using
//generate a `IntBinarySearchTree` binary search tree of `int` values
genny -in binarysearchtree.go -out binarysearchtree-int.go gen "Item=int"
//generate a `StringBinarySearchTree` binary search tree of `string` values
genny -in binarysearchtree.go -out binarysearchtree-string.go gen "Item=string"I wrote 20 books to help you become a better developer:
- Astro Handbook
- HTML Handbook
- Next.js Pages Router Handbook
- Alpine.js Handbook
- HTMX Handbook
- TypeScript Handbook
- React Handbook
- SQL Handbook
- Git Cheat Sheet
- Laravel Handbook
- Express Handbook
- Swift Handbook
- Go Handbook
- PHP Handbook
- Python Handbook
- Linux Commands Handbook
- C Handbook
- JavaScript Handbook
- CSS Handbook
- Node.js Handbook