Linux commands: who
A quick guide to the `who` command, used to show the users logged to the system
The who command displays the users logged in to the system.
Unless you’re using a server multiple people have access to, chances are you will be the only user logged in, multiple times:
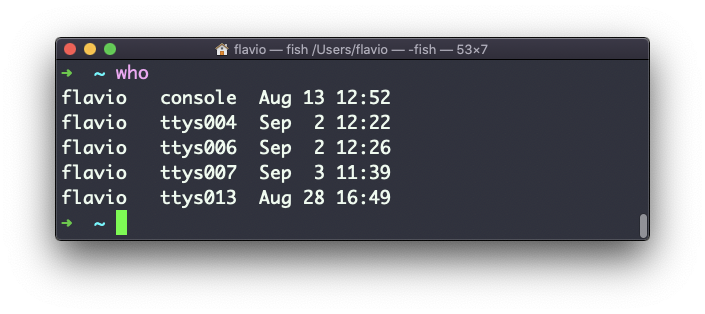
Why multiple times? Because each shell opened will count as an access.
You can see the name of the terminal used, and the time/day the session was started.
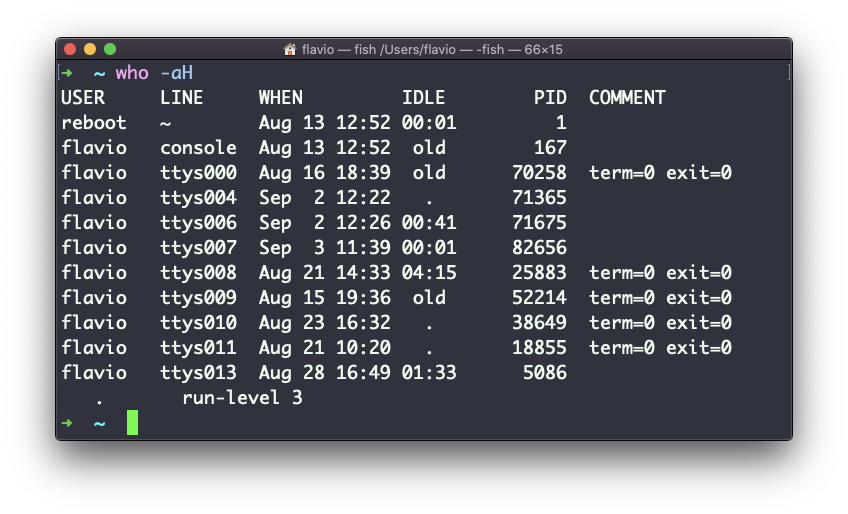
The -aH flags will tell who to display more information, including the idle time and the process ID of the terminal:
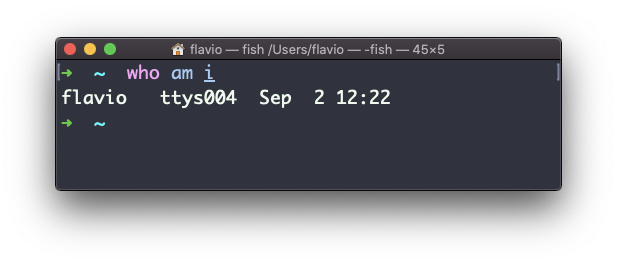
The special who am i command will list the current terminal session details:
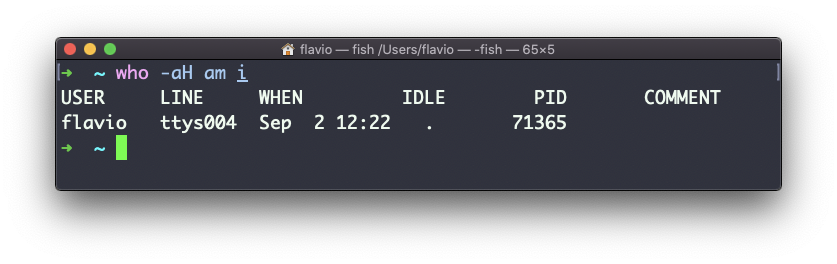
The
whocommand works on Linux, macOS, WSL, and anywhere you have a UNIX environment
→ I wrote 17 books to help you become a better developer:
- C Handbook
- Command Line Handbook
- CSS Handbook
- Express Handbook
- Git Cheat Sheet
- Go Handbook
- HTML Handbook
- JS Handbook
- Laravel Handbook
- Next.js Handbook
- Node.js Handbook
- PHP Handbook
- Python Handbook
- React Handbook
- SQL Handbook
- Svelte Handbook
- Swift Handbook
Also, JOIN MY CODING BOOTCAMP, an amazing cohort course that will be a huge step up in your coding career - covering React, Next.js - next edition February 2025