Using WebSockets with Node.js
WebSockets are an alternative to HTTP communication in Web Applications. They offer a long lived, bidirectional communication channel between client and server.
WebSockets are an alternative to HTTP communication in Web Applications.
They offer a long lived, bidirectional communication channel between client and server.
Once established, the channel is kept open, offering a very fast connection with low latency and overhead.
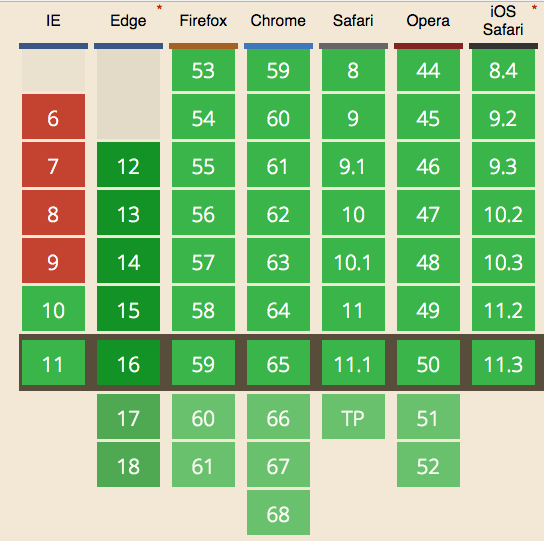
Browser support for WebSockets
WebSockets are supported by all modern browsers.
How WebSockets differ from HTTP
HTTP is a very different protocol, and also a different way of communicate.
HTTP is a request/response protocol: the server returns some data when the client requests it.
With WebSockets:
- the server can send a message to the client without the client explicitly requesting something
- the client and the server can talk to each other simultaneously
- very little data overhead needs to be exchanged to send messages. This means a low latency communication.
WebSockets are great for real-time and long-lived communications.
HTTP is great for occasional data exchange and interactions initiated by the client.
HTTP is much simpler to implement, while WebSockets require a bit more overhead.
Secured WebSockets
Always use the secure, encrypted protocol for WebSockets, wss://.
ws:// refers to the unsafe WebSockets version (the http:// of WebSockets), and should be avoided for obvious reasons.
Create a new WebSockets connection
const url = 'wss://myserver.com/something'
const connection = new WebSocket(url)
connection is a WebSocket object.
When the connection is successfully established, the open event is fired.
Listen for it by assigning a callback function to the onopen property of the connection object:
connection.onopen = () => {
//...
}
If there’s any error, the onerror function callback is fired:
connection.onerror = error => {
console.log(`WebSocket error: ${error}`)
}
Sending data to the server using WebSockets
Once the connection is open, you can send data to the server.
You can do so conveniently inside the onopen callback function:
connection.onopen = () => {
connection.send('hey')
}
Receiving data from the server using WebSockets
Listen with a callback function on onmessage, which is called when the message event is received:
connection.onmessage = e => {
console.log(e.data)
}
Implement a WebSockets server in Node.js
ws is a popular WebSockets library for Node.js.
We’ll use it to build a WebSockets server. It can also be used to implement a client, and use WebSockets to communicate between two backend services.
Easily install it using
yarn init
yarn add ws
The code you need to write is very little:
const WebSocket = require('ws')
const wss = new WebSocket.Server({ port: 8080 })
wss.on('connection', ws => {
ws.on('message', message => {
console.log(`Received message => ${message}`)
})
ws.send('ho!')
})
This code creates a new server on port 8080 (the default port for WebSockets), and adds a callback function when a connection is established, sending ho! to the client, and logging the messages it receives.
See a live example on Glitch
Here is a live example of a WebSockets server: https://glitch.com/edit/#!/flavio-websockets-server-example
Here is a WebSockets client that interacts with the server: https://glitch.com/edit/#!/flavio-websockets-client-example
→ I wrote 17 books to help you become a better developer:
- C Handbook
- Command Line Handbook
- CSS Handbook
- Express Handbook
- Git Cheat Sheet
- Go Handbook
- HTML Handbook
- JS Handbook
- Laravel Handbook
- Next.js Handbook
- Node.js Handbook
- PHP Handbook
- Python Handbook
- React Handbook
- SQL Handbook
- Svelte Handbook
- Swift Handbook
Also, JOIN MY CODING BOOTCAMP, an amazing cohort course that will be a huge step up in your coding career - covering React, Next.js - next edition February 2025