Web Scraping using Node.js and Puppeteer
A short introductory tutorial to Web Scraping
Web Scraping is the task of downloading a web page and extracting some kind of information from it.
I recently made a little project with an Arduino board with a LCD display attached. Using Johnny-Five, which lets us program the Arduino using Node.js, I wanted to fetch the temperature measured at the top of a mountain, and show it on the Arduino board.
I used Puppeteer to do the task of scraping. Puppeteer is a great tool built by Google. It’s a Node library we can use to control a headless Chrome instance.
This means we are basically use Chrome, but programmatically.
There are many practical uses for Puppeteer, including automating testing, make screenshots, create server-side rendered versions of single page apps, and more.
Start by installing it using
npm install puppeteerIn a Node.js file, require it:
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');then we can use the launch() method to create a browser instance:
(async () => {
const browser = await puppeteer.launch()
})()We use await, and so we must wrap this method call in an async function, which we immediately invoke.
Next we can use the newPage() method on the browser object to get the page object:
(async () => {
const browser = await puppeteer.launch()
const page = await browser.newPage()
})()Next up we call the goto() method on the page object to load that page:
(async () => {
const browser = await puppeteer.launch()
const page = await browser.newPage()
await page.goto('https://website.com')
})()Finally, we can get the page content calling the evaluate() method of page. This method takes a callback function where we can add the code needed to retrieve the elements of the page we need. The function is executed in the context of a page, so we have access to document and all the browser APIs. We return a new object, and this will be the result of our evaluate() method call.
We can use the Selectors API and retrieve data from the page.
(async () => {
const browser = await puppeteer.launch()
const page = await browser.newPage()
await page.goto('https://website.com')
const result = await page.evaluate(() => {
//...
})
})()Let’s get to the particular problem I have. This is the page which hosts the meteo station, located on the top of a mountain at 3315m: http://www.meteocentrale.ch/it/europa/svizzera/meteo-corvatsch/details/S067910/
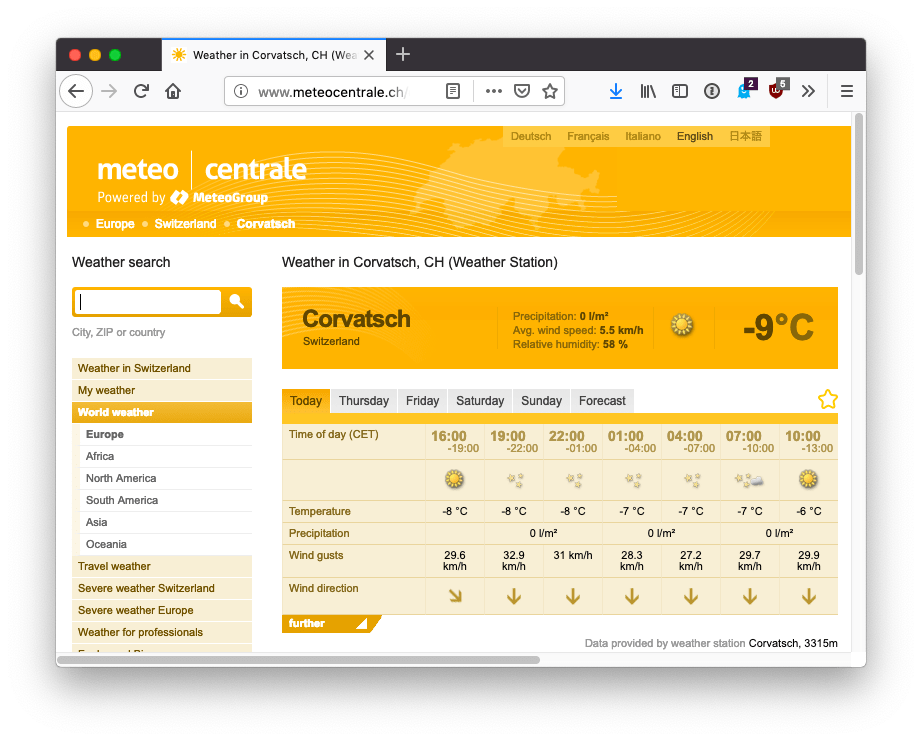
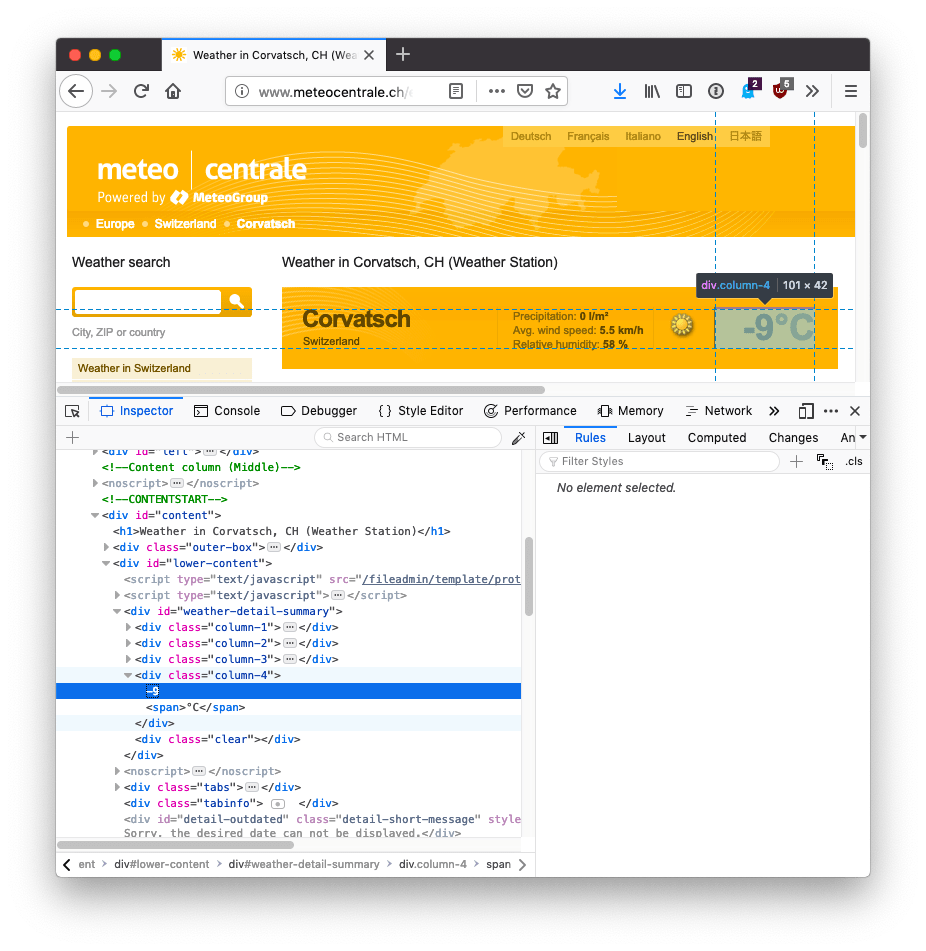
I want to get that -9°C text. Using the browser inspector I can see it has a column-4 class attached. It’s not an ideal class name, as it’s not meaningful, and might change if they decide to add a new column, but this is what we got:
This is the complete code up to now:
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
(async () => {
const browser = await puppeteer.launch()
const page = await browser.newPage()
await page.goto('http://www.meteocentrale.ch/it/europa/svizzera/meteo-corvatsch/details/S067910/')
const result = await page.evaluate(() => {
let temperature = document.querySelector('.column-4').innerText
return {
temperature
}
})
console.log(result)
browser.close()
})()If we run this code, result will have this value:
{
temperature: '-9°C'
}or whatever the temperature is right now.
I wrote 19 books to help you become a better developer:
- HTML Handbook
- Next.js Pages Router Handbook
- Alpine.js Handbook
- HTMX Handbook
- TypeScript Handbook
- React Handbook
- SQL Handbook
- Git Cheat Sheet
- Laravel Handbook
- Express Handbook
- Swift Handbook
- Go Handbook
- PHP Handbook
- Python Handbook
- Linux Commands Handbook
- C Handbook
- JavaScript Handbook
- CSS Handbook
- Node.js Handbook