Working with Docker Containers from the command line
THE SOLOPRENEUR MASTERCLASS
Now open with 50% OFF launch discount!
The Docker Desktop application is awesome to work with containers locally via a graphical interface.
You are not required to use it. You can use the CLI commands.
The docker ps command lists the currently running containers:
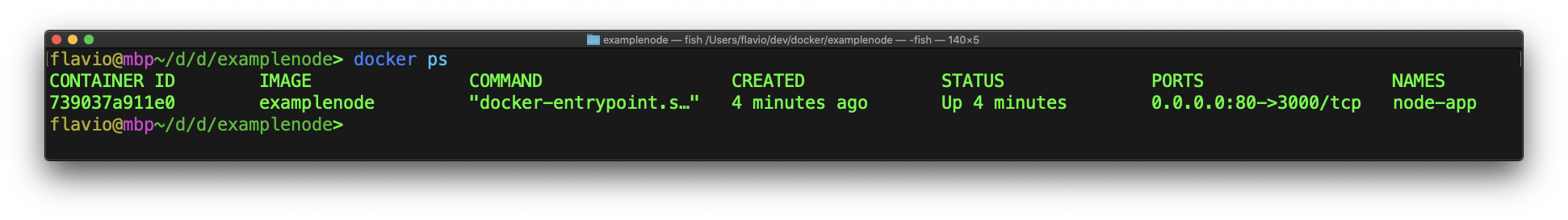
This is the same as running
docker container ls.
In this case, container with name node-app and ID 739037a911e0 generated from the image examplenode, created 4 minutes ago, is up since 4 minutes, and the port 80 of the host machine is mapped to the container port 3000 using the TCP protocol.
When you know the contained ID, you can stop the container by running
docker container stop <ID>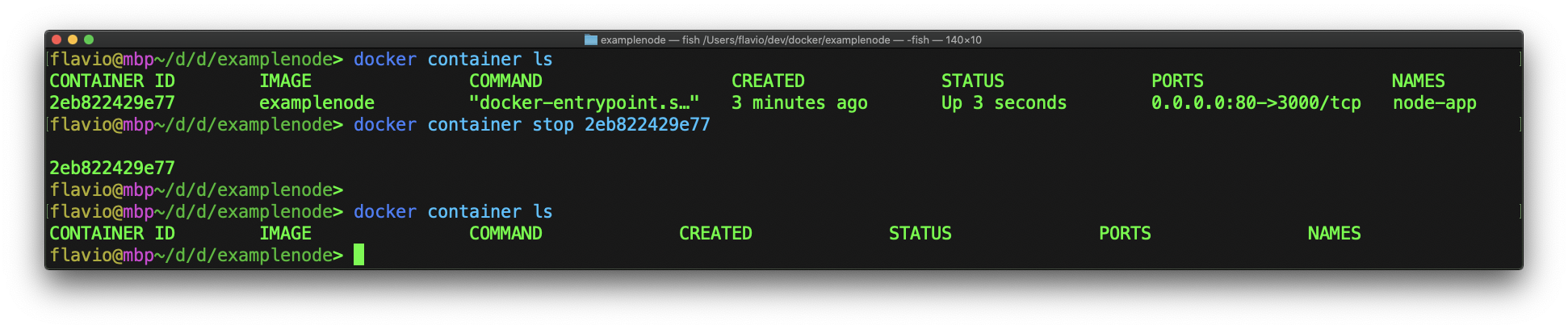
Once a container is stopped, you can see it using docker container ls -a:
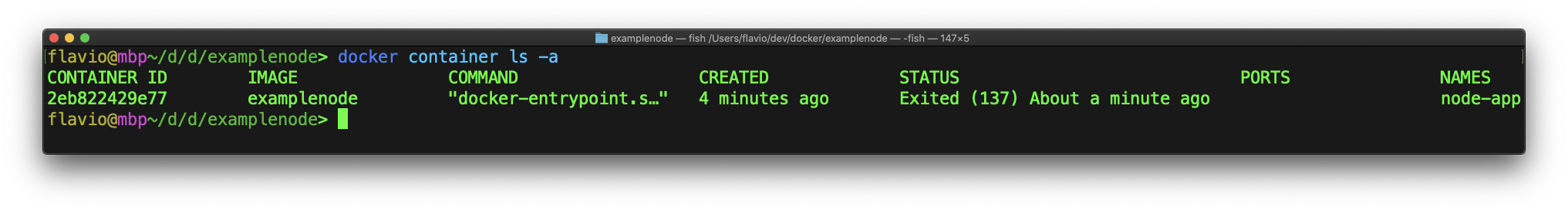
And you can remove it using docker container rm:
docker container rm <ID>You can inspect all the details about a container running docker inspect:
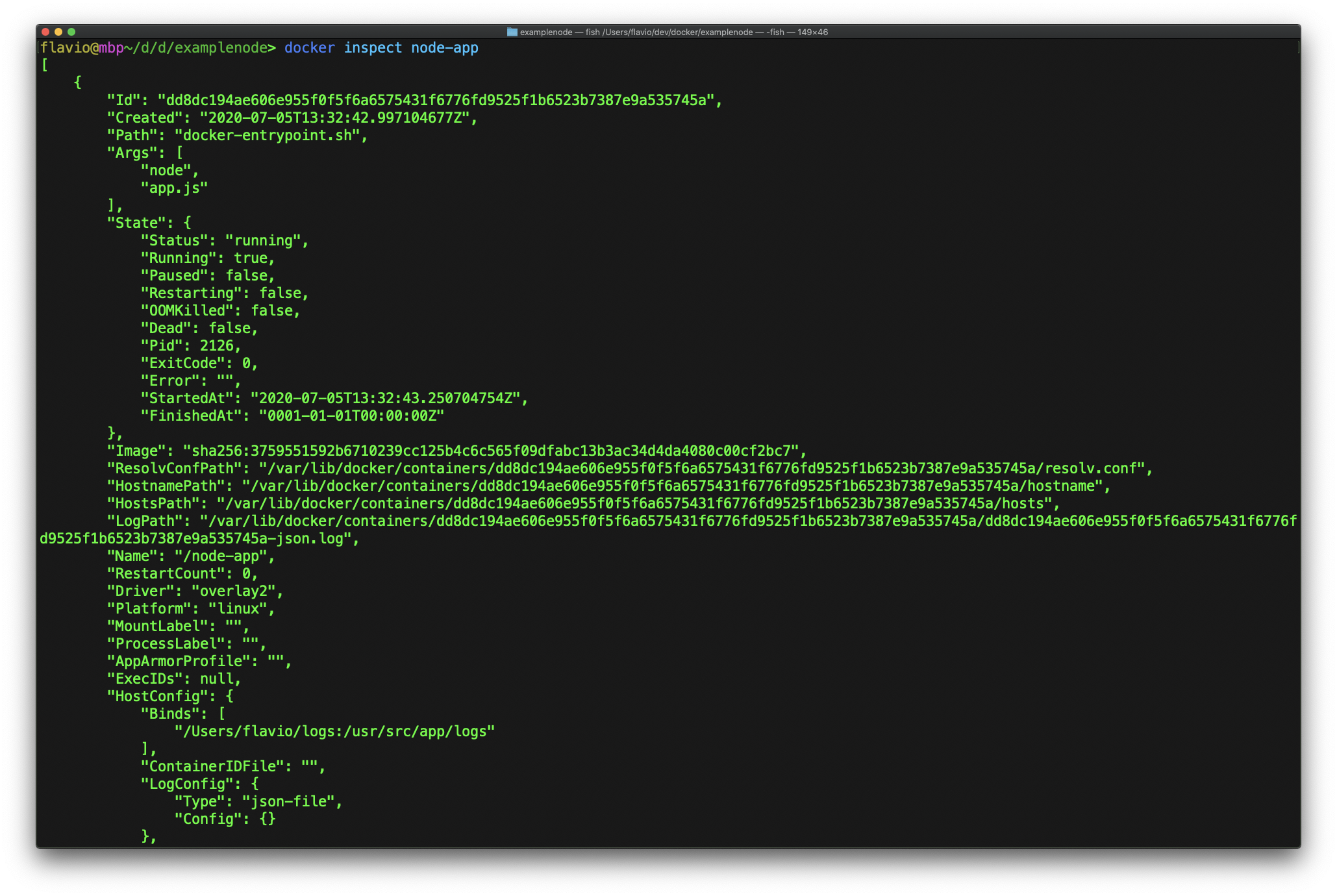
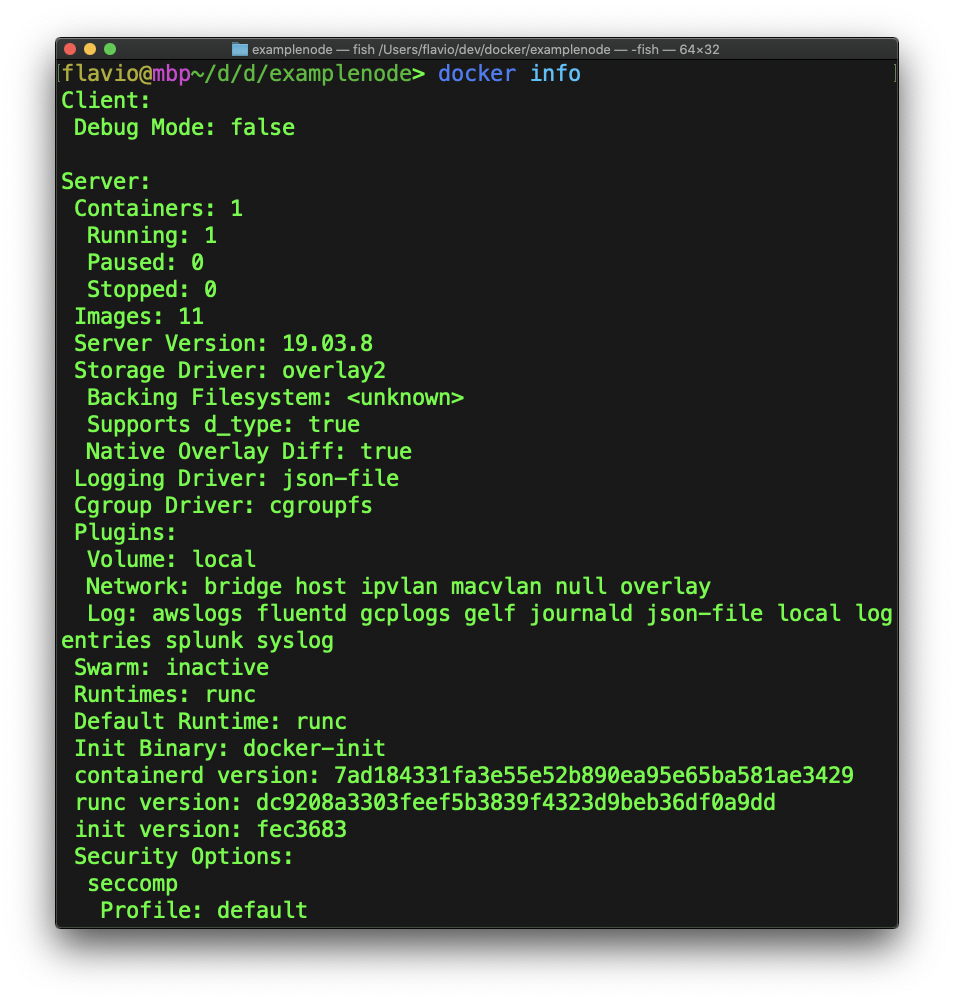
Another useful CLI command is docker info which gives you lots of information about the current state of your Docker installation, including the number of containers and images.
I wrote 20 books to help you become a better developer:
- Astro Handbook
- HTML Handbook
- Next.js Pages Router Handbook
- Alpine.js Handbook
- HTMX Handbook
- TypeScript Handbook
- React Handbook
- SQL Handbook
- Git Cheat Sheet
- Laravel Handbook
- Express Handbook
- Swift Handbook
- Go Handbook
- PHP Handbook
- Python Handbook
- Linux Commands Handbook
- C Handbook
- JavaScript Handbook
- CSS Handbook
- Node.js Handbook