Working with Docker Images from the command line
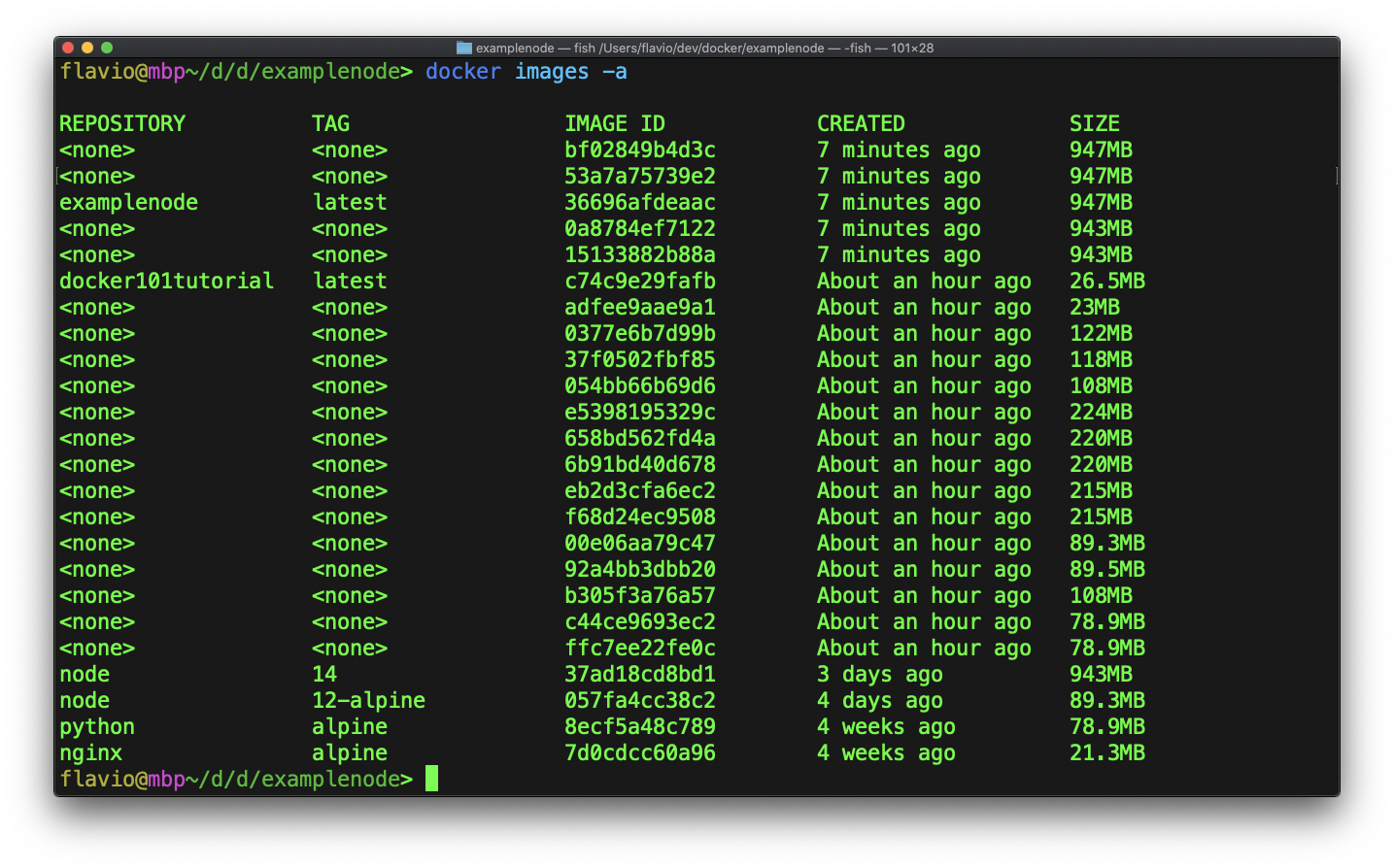
You can list all the images you have downloaded or installed using the
docker images -acommand:
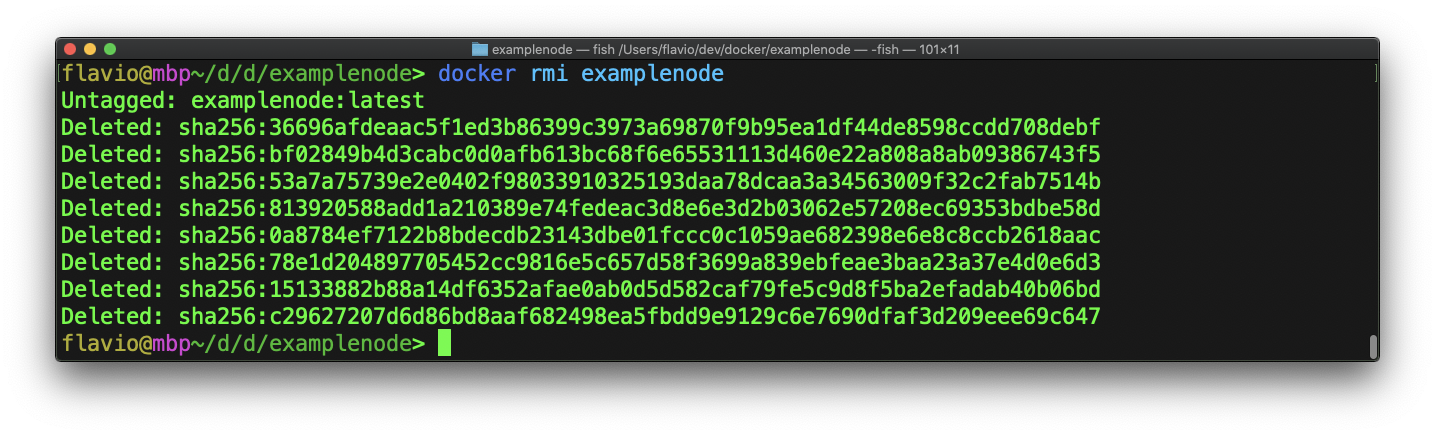
You can remove an image with docker rmi command, passing the name of the image you want to remove. This will remove the image.
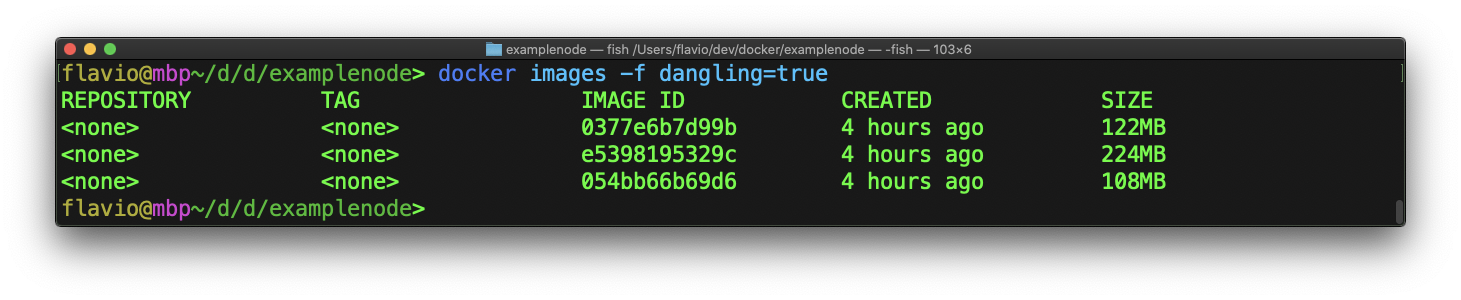
Sometimes when testing and developing, some images become dangling, which means untagged images. They can always be safely removed to free disk space.
Running docker images -f dangling=true will list them:
And you can clear them with docker rmi $(docker images -f dangling=true -q). This command will only eliminate dangling images used in containers, even if not currently running.
docker system prune -a, which is also a commonly used way to remove images, will also remove images not referenced by any container, which might remove images you might want to keep, even just to rollback to previous versions of an image.
You can also remove all images using docker rmi $(docker images -a -q) if you want to clean everything, which might be nice during your first tests and experiments with Docker.
download all my books for free
- javascript handbook
- typescript handbook
- css handbook
- node.js handbook
- astro handbook
- html handbook
- next.js pages router handbook
- alpine.js handbook
- htmx handbook
- react handbook
- sql handbook
- git cheat sheet
- laravel handbook
- express handbook
- swift handbook
- go handbook
- php handbook
- python handbook
- cli handbook
- c handbook
subscribe to my newsletter to get them
Terms: by subscribing to the newsletter you agree the following terms and conditions and privacy policy. The aim of the newsletter is to keep you up to date about new tutorials, new book releases or courses organized by Flavio. If you wish to unsubscribe from the newsletter, you can click the unsubscribe link that's present at the bottom of each email, anytime. I will not communicate/spread/publish or otherwise give away your address. Your email address is the only personal information collected, and it's only collected for the primary purpose of keeping you informed through the newsletter. It's stored in a secure server based in the EU. You can contact Flavio by emailing [email protected]. These terms and conditions are governed by the laws in force in Italy and you unconditionally submit to the jurisdiction of the courts of Italy.