CSS box-sizing: border-box
AI workshop
join cohort #1
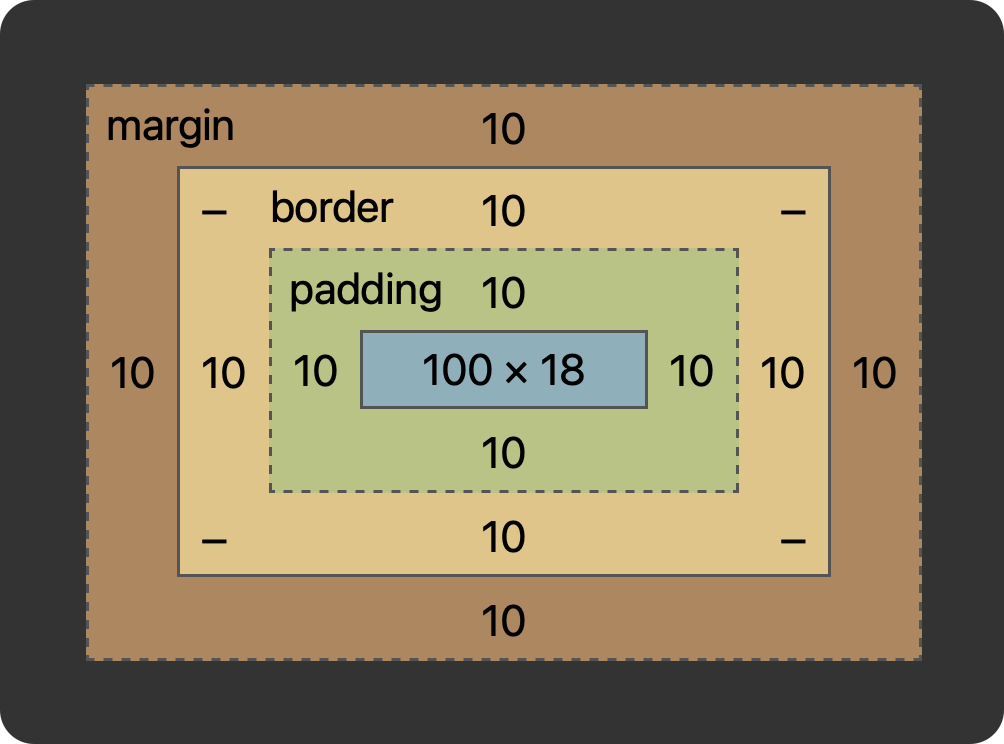
By default, if you set a width (or height) on the element, that is going to be applied to the content area.
This does not include the padding, border, and margin, which are added on top.
For example, I set this CSS on a p element:
p {
width: 100px;
padding: 10px;
border: 10px solid black;
margin: 10px;
}and here’s what’s applied by the browser:
You can change this behavior by setting the box-sizing property. If you set that to border-box, width and height calculation include the padding and the border.
Here’s what it means on the previous example:
p {
box-sizing: border-box;
width: 100px;
padding: 10px;
border: 10px solid black;
margin: 10px;
}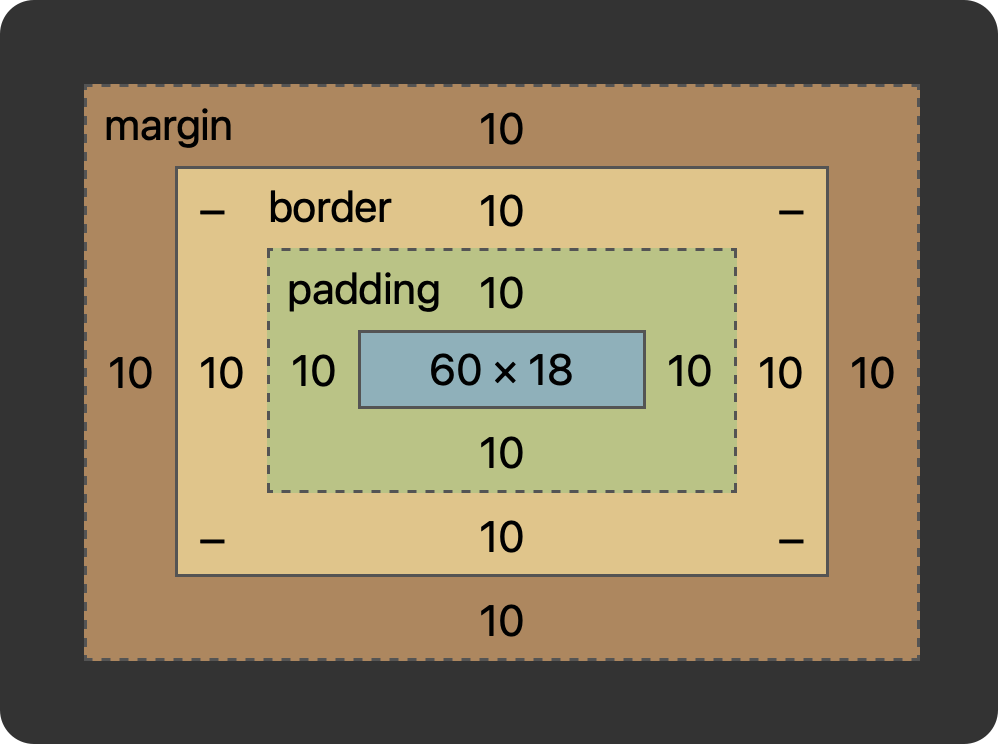
See? The actual element size is now 60 because it’s 100 - 10 * 2 (padding) - 10 * 2 (border).
Only the margin is left out, which is reasonable since in our mind we also typically see that as a separate thing: margin is outside of the box of the element.
This property is a small change but has a big impact in how you calculate your elements dimensions.
If you like using it, you can apply it to every element on the page with this CSS rule, that applies this to every element
*,
*:before,
*:after {
box-sizing: border-box;
}I wrote 20 books to help you become a better developer:
- Astro Handbook
- HTML Handbook
- Next.js Pages Router Handbook
- Alpine.js Handbook
- HTMX Handbook
- TypeScript Handbook
- React Handbook
- SQL Handbook
- Git Cheat Sheet
- Laravel Handbook
- Express Handbook
- Swift Handbook
- Go Handbook
- PHP Handbook
- Python Handbook
- Linux Commands Handbook
- C Handbook
- JavaScript Handbook
- CSS Handbook
- Node.js Handbook