Linux commands: du
A quick guide to the `du` command, used to calculate the space usage of files and directories
THE SOLOPRENEUR MASTERCLASS
Now open with 50% OFF launch discount!
The du command will calculate the size of a directory as a whole:
du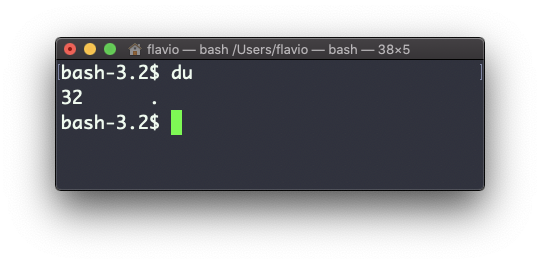
The 32 number here is a value expressed in bytes.
Running du * will calculate the size of each file individually:
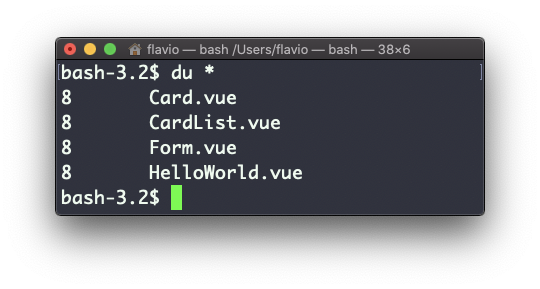
You can set du to display values in MegaBytes using du -m, and GigaBytes using du -g.
The -h option will show a human-readable notation for sizes, adapting to the size:
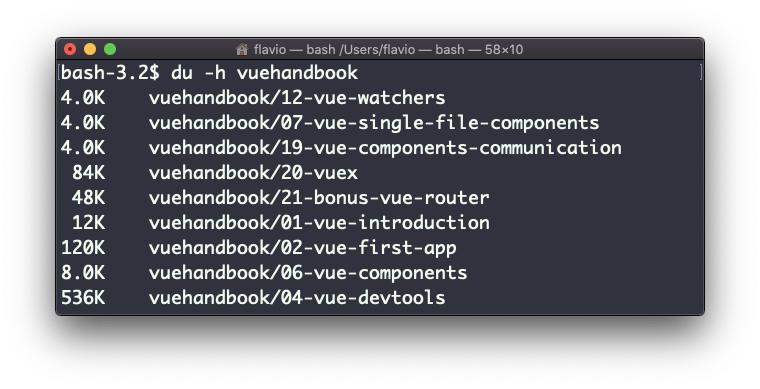
Adding the -a option will print the size of each file in the directories, too:
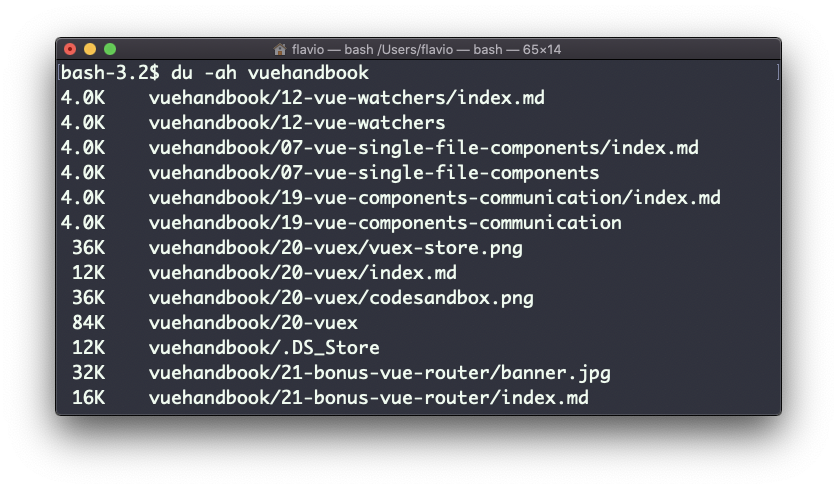
A handy thing is to sort the directories by size:
du -h <directory> | sort -nrand then piping to head to only get the first 10 results:
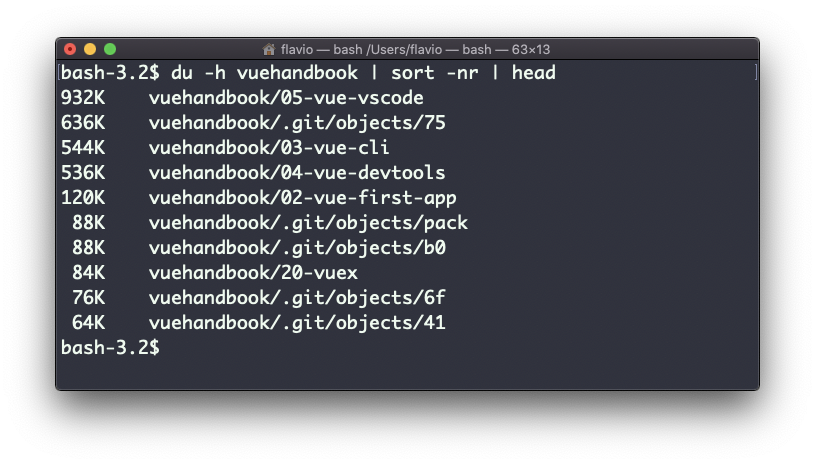
The
ducommand works on Linux, macOS, WSL, and anywhere you have a UNIX environment
I wrote 20 books to help you become a better developer:
- Astro Handbook
- HTML Handbook
- Next.js Pages Router Handbook
- Alpine.js Handbook
- HTMX Handbook
- TypeScript Handbook
- React Handbook
- SQL Handbook
- Git Cheat Sheet
- Laravel Handbook
- Express Handbook
- Swift Handbook
- Go Handbook
- PHP Handbook
- Python Handbook
- Linux Commands Handbook
- C Handbook
- JavaScript Handbook
- CSS Handbook
- Node.js Handbook