Linux commands: sudo
A quick guide to the `sudo` command, used to run a command as another user
AI workshop
join cohort #1
sudo is commonly used to run a command as root.
You must be enabled to use sudo, and once you do, you can run commands as root by entering your user’s password (not the root user password).
The permissions are highly configurable, which is great especially in a multi-user server environment, and some users can be granted access to running specific commands through sudo.
For example you can edit a system configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/hostswhich would otherwise fail to save since you don’t have the permissions for it.
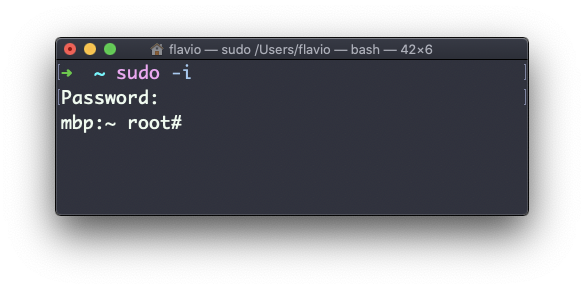
You can run sudo -i to start a shell as root:
You can use sudo to run commands as any user. root is the default, but use the -u option to specify another user:
sudo -u flavio ls /Users/flavioThe
sudocommand works on Linux, macOS, WSL, and anywhere you have a UNIX environment
I wrote 20 books to help you become a better developer:
- Astro Handbook
- HTML Handbook
- Next.js Pages Router Handbook
- Alpine.js Handbook
- HTMX Handbook
- TypeScript Handbook
- React Handbook
- SQL Handbook
- Git Cheat Sheet
- Laravel Handbook
- Express Handbook
- Swift Handbook
- Go Handbook
- PHP Handbook
- Python Handbook
- Linux Commands Handbook
- C Handbook
- JavaScript Handbook
- CSS Handbook
- Node.js Handbook