How to use window.prompt()
How to use the prompt() API offered by browsers to let the user decide something
AI workshop
join cohort #1
prompt() lets us get input from the user.
This API dates back to the dawn of the Web, and is supported by every browser.
It’s very simple and I think it might come handy especially while prototyping an app, so you can just call a prompt() and be done with it, without setting up a form.
Here’s how it works: you call prompt()
You pass a string that represents the question we ask to the user:
prompt("How old are you?")This is how it looks in Chrome:
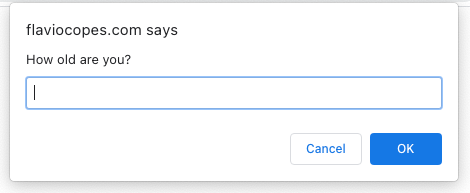
This is in Safari:
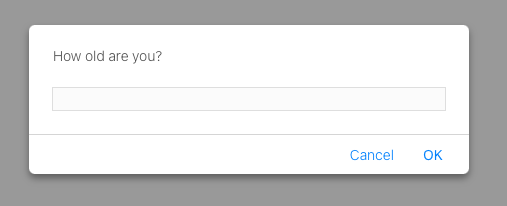
This is in Firefox:

As you can see, it’s different but the concept is the same
You should call
window.prompt(), but sincewindowis implicit,prompt()works
The browser blocks the script execution until the user enters something and clicks any of the OK or Cancel button. You can’t escape from that without clicking a button.
The value entered is then returned from this function, so we can assign it to a variable:
const age = prompt("How old are you?")You can pass a second parameter that’s the default value prefilled in the prompt:
const age = prompt("How old are you?", 18)If the user enters nothing and clicks OK, an empty string will be returned.
If the user clicks the Cancel button, the prompt() function call returns null
I wrote 20 books to help you become a better developer:
- Astro Handbook
- HTML Handbook
- Next.js Pages Router Handbook
- Alpine.js Handbook
- HTMX Handbook
- TypeScript Handbook
- React Handbook
- SQL Handbook
- Git Cheat Sheet
- Laravel Handbook
- Express Handbook
- Swift Handbook
- Go Handbook
- PHP Handbook
- Python Handbook
- Linux Commands Handbook
- C Handbook
- JavaScript Handbook
- CSS Handbook
- Node.js Handbook